
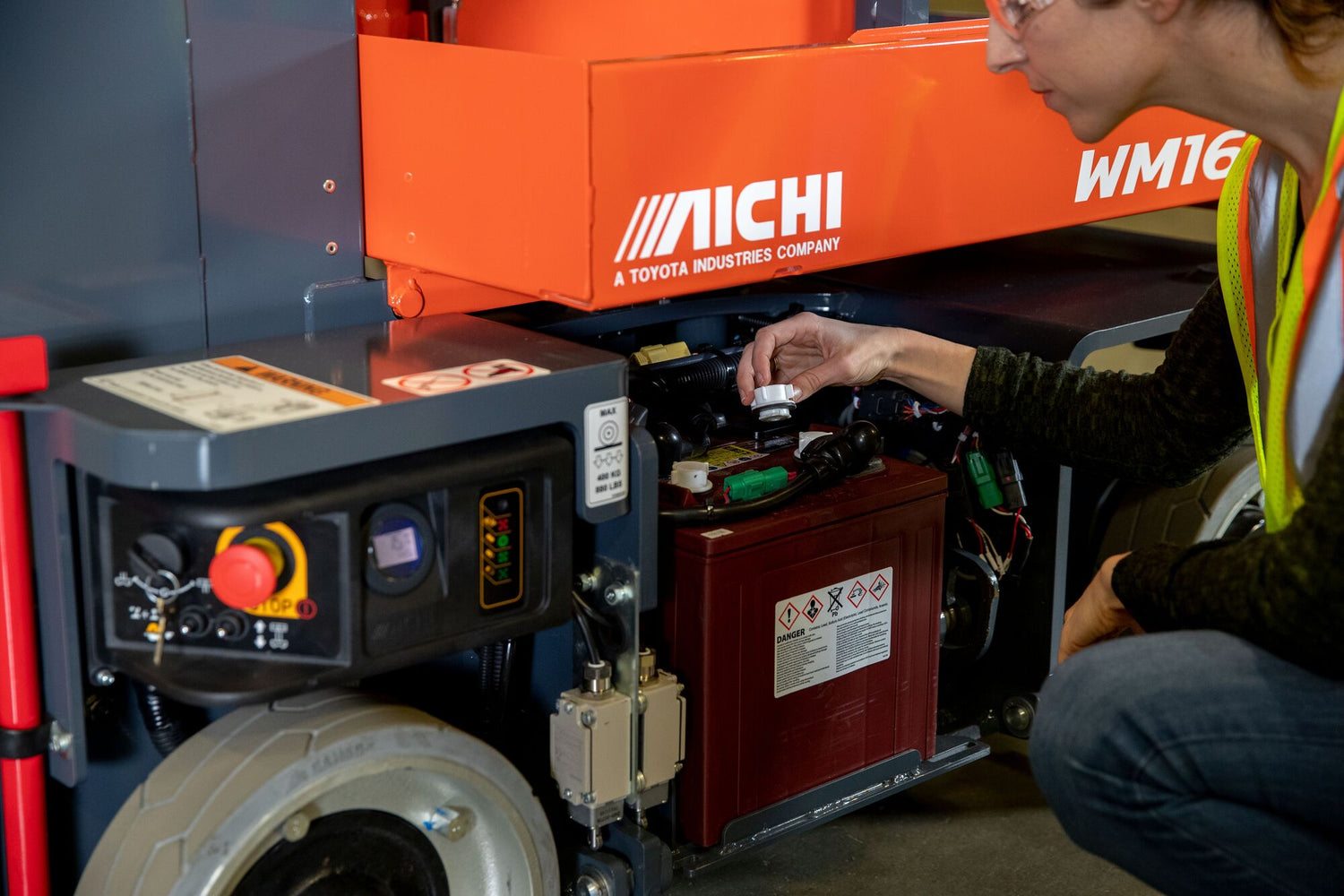
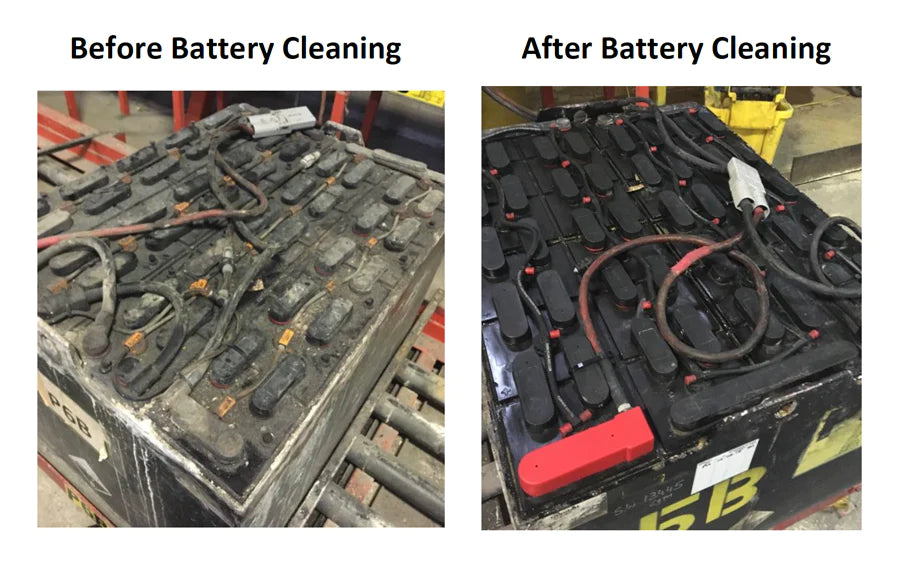
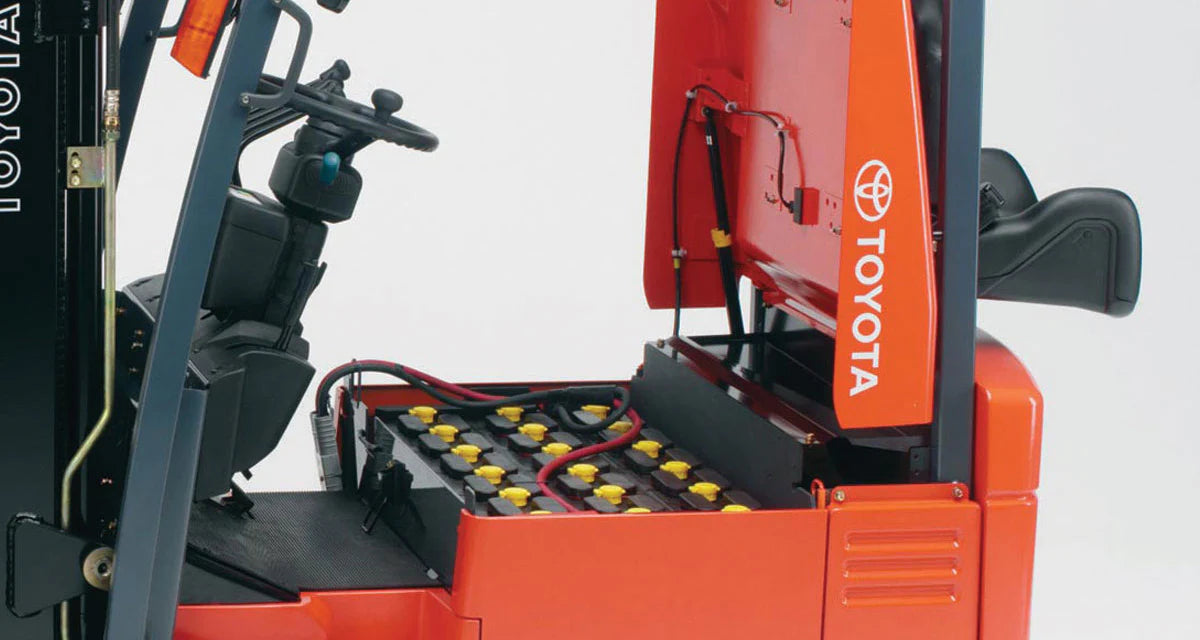
Protect your forklifts from corrosion and failure
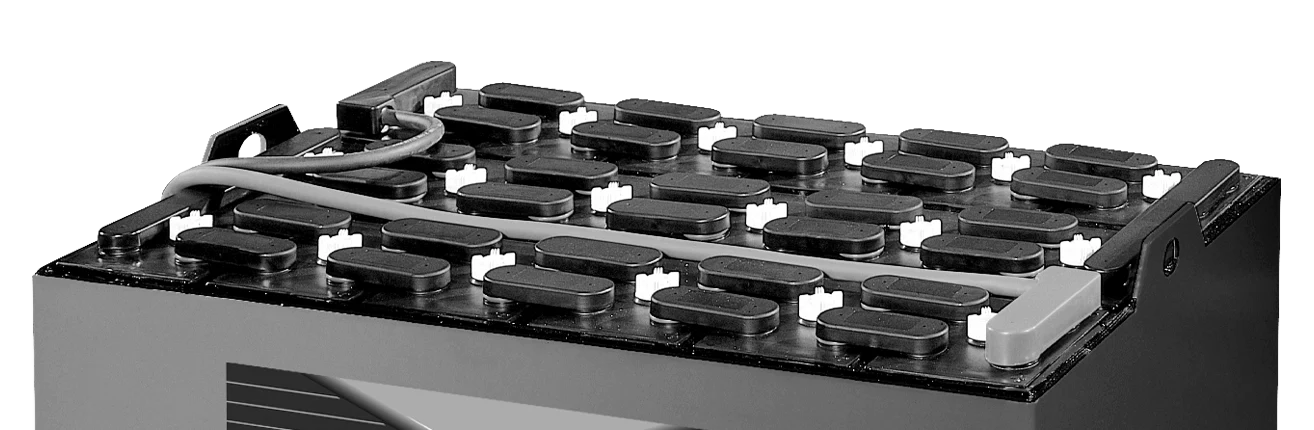
Many people think of cleaning forklift batteries as purely cosmetic task, but it’s far more important than that. Acid buildup...
Liftow Toronto
1400 Courtney Park Drive East
905-677-3270
1-800-387-3140
Branch Hours +
| Monday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |
| Tuesday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |
| Wednesday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |
| Thursday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |
| Friday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |
| Saturday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |
| Sunday | 7:30AM - 4:30PM |




Excellent service! They helped me find exactly what I needed in terms of forklift impact monitoring systems.
Sara Burt
Wow! Great service all-around. Customer relations seemed to be a top priority. They called to follow-up to ensure I was satisfied with their business. Much appreciated!
Nicole Loebach
I find the service we get from Liftow is top notch there technician are very knowledgeable about the equipment they sell. The sales team are very professional and were able to answer any question we had. I would not deal with no one else, they got the best forklifts on the market. Thanks for all the good service!
Stedman Letto
We have purchased two gently used electric walkies from Liftow and a used forklift, and we are extremely happy with the service and the equipment.
Caroline Bee
Seeing business through a customer's eyes is what I call customer vision - and that's what the Liftow team brings. Offering quality products and services in a customer focused way, adds long lasting value to those that look for and appreciate, a true bargain. They're a pleasure to work with.
Dan Cartmell
Good company to work with. The employees that I dealt with were knowledgeable. We rented a forklift to move some equipment internally and had absolutely no issues. Thanks again.
Darwin Cuneo

Many people think of cleaning forklift batteries as purely cosmetic task, but it’s far more important than that. Acid buildup...

In the world of landscaping and renovation, timelines are tight, budgets are fixed, and every tool on site must perform....
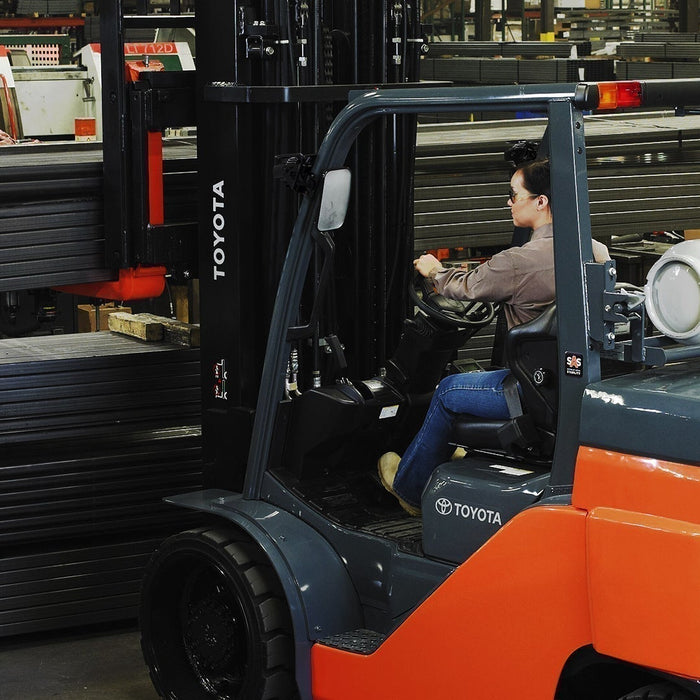

In today’s fast-moving warehousing and distribution landscape, your ability to adapt to shifting demands is essential. Whether you are managing...
Step 1 - Choose a:
PRODUCT TYPE
Step 2 - Choose a:
PRODUCT FAMILY
Step 3 - Choose a:
PRODUCT MODEL
Step 1 - Choose a:
PRODUCT TYPE
Step 2 - Choose a:
PRODUCT FAMILY
Step 3 - Choose a:
PRODUCT MODEL
Step 1 - Choose a:
PRODUCT TYPE
Step 2 - Choose a:
PRODUCT FAMILY
Step 3 - Choose a:
PRODUCT MODEL